Photo from academic.microsoft.com
Maxillary hypoplasia is a commonly seen dentofacial anomaly in patients with cleft lip and palate after surgical repair of the cleft anomaly. To facilitate large horizontal movements of the maxilla,… Click to show full abstract
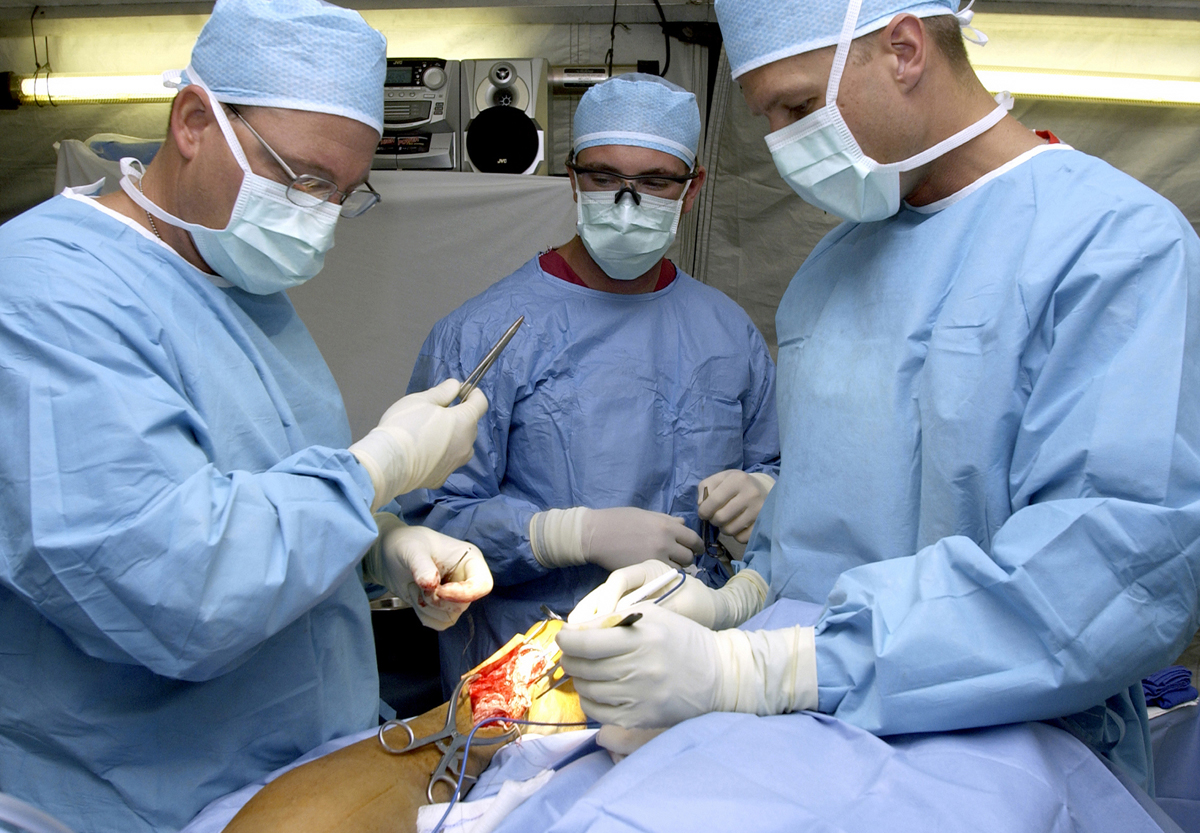
Maxillary hypoplasia is a commonly seen dentofacial anomaly in patients with cleft lip and palate after surgical repair of the cleft anomaly. To facilitate large horizontal movements of the maxilla, distraction osteogenesis is used to slowly stretch the soft tissue envelope with the skeletal advancement preventing tissue recoil and skeletal relapse. Internal distraction devices have the advantage of reducing the amount of physical and psychological stress placed on patients, families, and caregivers. The technique has been successful in producing stable results for large advancements of the facial skeleton when compared with conventional Le Fort I advancement and fixation of the maxilla.
Journal Title: Clinics in plastic surgery
Year Published: 2021
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!