Photo from wikipedia
Patients with short QT syndrome (SQTS) may present with syncope, ventricular fibrillation or sudden cardiac death. Six SQTS susceptibility genes, encoding cation channels, explain Click to show full abstract
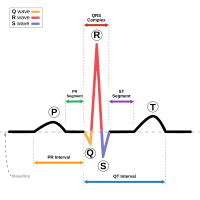
Patients with short QT syndrome (SQTS) may present with syncope, ventricular fibrillation or sudden cardiac death. Six SQTS susceptibility genes, encoding cation channels, explain <25% of SQTS cases. Here we identify a missense mutation in the anion exchanger (AE3)-encoding SLC4A3 gene in two unrelated families with SQTS. The mutation causes reduced surface expression of AE3 and reduced membrane bicarbonate transport. Slc4a3 knockdown in zebrafish causes increased cardiac pHi, short QTc, and reduced systolic duration, which is rescued by wildtype but not mutated SLC4A3. Mechanistic analyses suggest that an increase in pHi and decrease in [Cl−]i shortened the action potential duration. However, other mechanisms may also play a role. Altered anion transport represents a mechanism for development of arrhythmia and may provide new therapeutic possibilities.Mutations in potassium and calcium channel genes have been associated with cardiac arrhythmias. Here, Jensen et al. show that an anion transporter chloride-bicarbonate exchanger AE3 is also responsible for the genetically-induced mechanism of cardiac arrhythmia, suggesting new therapeutic targets for this disease
Journal Title: Nature Communications
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!