Photo from wikipedia
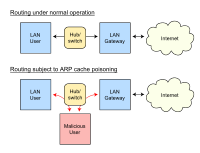
Address resolution protocol (ARP) cache poisoning is mostly used to perform man-in-the-middle (MITM) and denial of service (DoS) attacks for sniffing and network services disruption, respectively, in switch LAN networks.… Click to show full abstract
Address resolution protocol (ARP) cache poisoning is mostly used to perform man-in-the-middle (MITM) and denial of service (DoS) attacks for sniffing and network services disruption, respectively, in switch LAN networks. The former attack affects the privacy of a network user, whereas the latter attack causes huge damage to networks in terms of unavailability of services. There are many security solutions that provide protection against such type of attacks at firewall level with the assumption that an insider attack does not exist. However, the most damaging and severe attacks on universities database servers to well-known banking system have been caused by insider malicious users. In this study, the authors propose an agent-based ARP cache poisoning detection (AACPD) scheme that detects the MITM and DoS attacks in a switch LAN environment. The objective of this scheme is to provide protection from insider malicious users. The proposed AACPD is compared with similar existing schemes in a real-time environment. The experimental results show that AACPD efficiently and accurately detects attackers with minimum effect on network performance as compared to similar existing schemes.
Journal Title: IET Networks
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!