Photo from wikipedia
Objective: This paper presents a fast approach to detect QRS complexes based on a simple analysis of the temporal ECG structure. Methods: The ECG is processed through several steps involving… Click to show full abstract
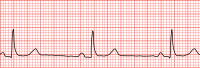
Objective: This paper presents a fast approach to detect QRS complexes based on a simple analysis of the temporal ECG structure. Methods: The ECG is processed through several steps involving noise removal, feature detection, and feature analysis. The obtained feature set, which holds most of the ECG information while requiring low data storage, constitutes a lossy compressed version of the ECG. Results: The experiments, performed using 12 different ECG databases, emphasize the advantages of our proposal. For example, 130-min ECG recordings are processed in average in 0.77 s. Also, sensitivities and positive predictions surpass 99.9% in some databases, and a global data saving of 90.35% is achieved. Conclusion and significance: When compared to other approaches, this study offers a parameterless and computationally efficient alternative for QRS complex detection and lossy ECG compression. Moreover, some of the presented techniques are general enough to be used by other ECG analysis tools. Finally, the documented source code corresponding to this study is publicly available.
Journal Title: IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!