Photo from wikipedia
Tissue engineering has progressed tremendously over recent decades through the generation of functional tissue analogs. Traditional approaches based on seeding cells into scaffold are limited in their capacity to produce… Click to show full abstract
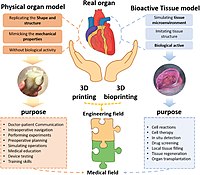
Tissue engineering has progressed tremendously over recent decades through the generation of functional tissue analogs. Traditional approaches based on seeding cells into scaffold are limited in their capacity to produce tissues with precise biomimetic properties. Three-dimensional (3D) bioprinting is one kind of fabrication technology used to precisely dispense cell-laden biomaterials for the construction of functional tissues or organs. In recent years, much research progress has been made in 3D bioprinting technology and its application in generating tissue analogs, including skin, heart valves, blood vessels, bone, and cardiac tissue. However, it still faces many technical challenges. In this review, we introduce the current progress in 3D bioprinting technology and focus on biomaterials and their potential applications in regenerative medicine and drug discovery. Current challenges are also discussed.
Journal Title: SLAS Technology
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!