Photo from wikipedia
Importance COVID-19 is associated with a high incidence of thrombotic events; however, the need for extended thromboprophylaxis after hospitalization remains unclear. Objective To quantify the rate of postdischarge arterial and… Click to show full abstract
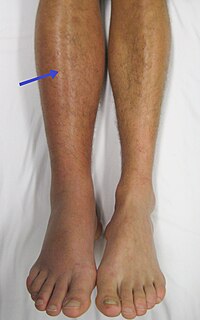
Importance COVID-19 is associated with a high incidence of thrombotic events; however, the need for extended thromboprophylaxis after hospitalization remains unclear. Objective To quantify the rate of postdischarge arterial and venous thromboembolism in patients with COVID-19, identify the factors associated with the risk of postdischarge venous thromboembolism, and evaluate the association of postdischarge anticoagulation use with venous thromboembolism incidence. Design, Setting, and Participants This is a cohort study of adult patients hospitalized with COVID-19 confirmed by a positive SARS-CoV-2 test. Eligible patients were enrolled at 5 hospitals of the Henry Ford Health System from March 1 to November 30, 2020. Data analysis was performed from April to June 2021. Exposures Anticoagulant therapy after discharge. Main Outcomes and Measures New onset of symptomatic arterial and venous thromboembolic events within 90 days after discharge from the index admission for COVID-19 infection were identified using International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, Tenth Revision codes. Results In this cohort study of 2832 adult patients hospitalized with COVID-19, the mean (SD) age was 63.4 (16.7) years (IQR, 53-75 years), and 1347 patients (47.6%) were men. Thirty-six patients (1.3%) had postdischarge venous thromboembolic events (16 pulmonary embolism, 18 deep vein thrombosis, and 2 portal vein thrombosis). Fifteen (0.5%) postdischarge arterial thromboembolic events were observed (1 transient ischemic attack and 14 acute coronary syndrome). The risk of venous thromboembolism decreased with time (Mann-Kendall trend test, P < .001), with a median (IQR) time to event of 16 (7-43) days. There was no change in the risk of arterial thromboembolism with time (Mann-Kendall trend test, P = .37), with a median (IQR) time to event of 37 (10-63) days. Patients with a history of venous thromboembolism (odds ratio [OR], 3.24; 95% CI, 1.34-7.86), peak dimerized plasmin fragment D (D-dimer) level greater than 3 μg/mL (OR, 3.76; 95% CI, 1.86-7.57), and predischarge C-reactive protein level greater than 10 mg/dL (OR, 3.02; 95% CI, 1.45-6.29) were more likely to experience venous thromboembolism after discharge. Prescriptions for therapeutic anticoagulation at discharge were associated with reduced incidence of venous thromboembolism (OR, 0.18; 95% CI, 0.04-0.75; P = .02). Conclusions and Relevance Although extended thromboprophylaxis in unselected patients with COVID-19 is not supported, these findings suggest that postdischarge anticoagulation may be considered for high-risk patients who have a history of venous thromboembolism, peak D-dimer level greater than 3 μg/mL, and predischarge C-reactive protein level greater than 10 mg/dL, if their bleeding risk is low.
Journal Title: JAMA network open
Year Published: 2021
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!