Photo from wikipedia
Key Points Question How commonly are hyperosmolar therapies used in the management of severe traumatic brain injury in children, and which agent—mannitol or hypertonic saline solution—is associated with greater decreases… Click to show full abstract
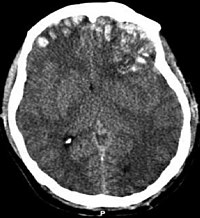
Key Points Question How commonly are hyperosmolar therapies used in the management of severe traumatic brain injury in children, and which agent—mannitol or hypertonic saline solution—is associated with greater decreases in intracranial pressure (ICP) and/or increases in cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP)? Findings In this comparative effectiveness research study of 1000 consecutive children with traumatic brain injury, more than 77% of the study population received hyperosmolar therapies during the ICP treatment phase of their care, and almost 2500 bolus administrations of 3% hypertonic saline and mannitol were analyzed. Hypertonic saline was associated with decreased ICP, whereas hypertonic saline and mannitol had similar observed effectiveness for CPP. Meaning This study of children with severe traumatic brain injury found that bolus administration of hypertonic saline was associated with superior ICP and CPP outcomes.
Journal Title: JAMA Network Open
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!