Photo from wikipedia
Here, we developed a method for measuring the in vivo redox state of the plastoquinone (PQ) pool in the cyanobacteria Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Cells were illuminated on a glass… Click to show full abstract
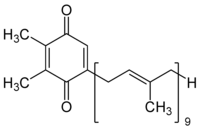
Here, we developed a method for measuring the in vivo redox state of the plastoquinone (PQ) pool in the cyanobacteria Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Cells were illuminated on a glass fiber filter, PQ was extracted with ethyl acetate and determined with HPLC. Control samples with fully oxidized and reduced photoactive PQ pool were prepared by far‐red and high light treatments, respectively, or by blocking the photosynthetic electron transfer chemically before or after PQ in moderate light. The photoactive pool comprised 50% of total PQ. We find that the PQ pool of cyanobacteria behaves under light treatments qualitatively similarly as in plant chloroplasts, is less reduced during growth under high than under ambient CO2 and remains partly reduced in darkness.
Journal Title: FEBS Letters
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!