Photo from wikipedia
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a chronic and progressive neurodegenerative disease, characterized by irreversible cognitive impairment, memory loss, and behavioral disturbances, ultimately resulting in death. The critical roles of glycogen synthase… Click to show full abstract
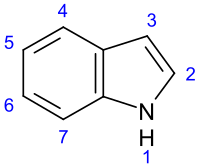
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a chronic and progressive neurodegenerative disease, characterized by irreversible cognitive impairment, memory loss, and behavioral disturbances, ultimately resulting in death. The critical roles of glycogen synthase kinase‐3β (GSK‐3β) in tau pathology have also received considerable attention. Based on molecular docking studies, a series of novel α‐carboline derivatives were designed, synthesized, and evaluated as GSK‐3β inhibitors for their various biological activities. Among them, compound ZCH‐9 showed the most potent inhibitory activity against GSK‐3β, with an IC50 value of 1.71 ± 0.09 µM. The cytotoxicity assay showed that ZCH‐9 had low cytotoxicity toward the cell lines SH‐SY5Y, HepG2, and HL‐7702. Moreover, Western blot analysis indicated that ZCH‐9 effectively inhibited hyperphosphorylation of the tau protein in okadaic acid‐treated SH‐SY5Y cells. The binding mode between ZCH‐9 and GSK‐3β was analyzed and further clarified throughout the molecular dynamics simulations. In general, these results suggested that the α‐carboline‐based small‐molecule compounds could serve as potential candidates targeting GSK‐3β for the treatment of AD.
Journal Title: Archiv der Pharmazie
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!