Photo from wikipedia
The application of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) for therapeutic use in visual‐related disorders and its underlying mechanisms in the visual cortex is under‐investigated. Additionally, there is little examination of… Click to show full abstract
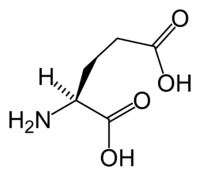
The application of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) for therapeutic use in visual‐related disorders and its underlying mechanisms in the visual cortex is under‐investigated. Additionally, there is little examination of rTMS adverse effects particularly with regards to visual and cognitive function. Neural plasticity is key in rehabilitation and recovery of function; thus, effective therapeutic strategies must be capable of modulating plasticity. Glutamate and γ‐aminobutyric acid (GABA)‐mediated changes in the balance between excitation and inhibition are prominent features in visual cortical plasticity.
Journal Title: Brain and Behavior
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!