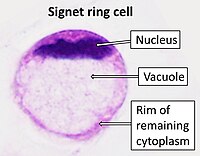
Photo from wikipedia
To get a better understanding of the genetic basis of primary signet ring cell carcinoma (SRCC) of the bladder, which is highly rare and not yet explored. First, by using… Click to show full abstract
To get a better understanding of the genetic basis of primary signet ring cell carcinoma (SRCC) of the bladder, which is highly rare and not yet explored. First, by using immunohistochemistry to find histological pathological characteristics. Second, a massively parallel whole‐exome sequencing (WES) was performed on a 58‐year‐old male patient who had painless macroscopic hematuria and was pathologically diagnosed with primary SRCC of the bladder, followed by comparing with genes of ordinary urothelial cancer (UC) from TCGA. Furthermore, a population‐based analysis using the SEER database was performed to investigate the prognosis (SRCC vs. UC). We identified 63 copy number variations (CNVs) with gain counts and 181 CNVs with loss counts. Totally 4515 mutations were discovered in C > T with a success rate of greater than 89%. The most frequently mutated pathway was RTK‐RAS which has 85 genes involved in carcinogenic signaling. Final screening on predisposing genes is performed after filtering based on ACMG. Moreover, several driver genes, including NBN, KCTD18, SPATA13, ANKRD36, OR2L5, MALRD1, and LSMEM1, were detected. Sanger sequencing of germline DNA revealed the presence of a mutant base A/G of OR2L5 in the sequence, which was discovered for the first time in primary SRCC of the bladder. Furthermore, the immunohistochemical profile showed that primary SRCC of the bladder were positive for CK7, CK20, GATA‐3, and expression of CK(AE1/AE2), EMA, and Ki67. In the SEER‐based study, the patients with primary SRCC of the bladder got a worse prognosis compared to those with UC with median months overall survival (OS) 14 vs. 41, respectively, P = 0001, even after adjusting the variables in the Cox regression model, the SRCC of the bladder showed worse survival HR = 1.119, 95% CI = (1.081–1.328), P = 0.0001. These results imply that suppression of potential driver mutations may be a viable adjuvant treatment approach for primary SRCC in the bladder in place of standard chemotherapy, a possibility that warrants further clinical investigation.
Journal Title: Cancer Medicine
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!