Photo from wikipedia
Abstract With increased application of DNA metabarcoding in biodiversity assessment, various laboratory protocols have been optimized, and their further evaluation is subject of current research. Homogenization of bulk samples and… Click to show full abstract
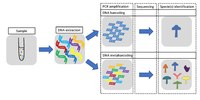
Abstract With increased application of DNA metabarcoding in biodiversity assessment, various laboratory protocols have been optimized, and their further evaluation is subject of current research. Homogenization of bulk samples and subsequent DNA extraction from a subsample of destructed tissue is a common first stage of the metabarcoding process. This can either be conducted using sample material soaked in a storage fixative, e.g., ethanol (here referred to as “wet” treatment) or from dried individuals (“dry”). However, it remains uncertain if perfect mixing and equal distribution of DNA within the tube is ensured during homogenization and to what extent incomplete mixing and resulting variations in tissue composition affect diversity assessments if only a fraction of the destructed sample is processed in the downstream metabarcoding workflow. Here we investigated the efficiency of homogenization under wet and dry conditions and tested how variations in destructed tissue composition might affect diversity assessments of complex arthropod samples. We considered five time intervals of Malaise trap bulk samples and process nine different subsamples of homogenized tissue (20 mg each) in both treatments. Results indicate a more consistent diversity assessment from dried material, but at the cost of a higher processing time. Both approaches detected comparable OTU diversity and revealed similar taxa compositions in a single tissue extraction. With an increased number of tissue subsamples during DNA extraction, OTU diversity increased for both approaches, especially for highly diverse samples obtained during the summer. Here, particularly the detection of small and low‐biomass taxa increased. The processing of multiple subsamples in the metabarcoding protocol can therefore be a helpful procedure to enhance diversity estimates and counteract taxonomic bias in biodiversity assessments. However, the process induces higher costs and time effort and the application in large‐scale biodiversity assessment, e.g., in monitoring schemes needs to be considered on project‐specific prospects.
Journal Title: Ecology and Evolution
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!