Photo from wikipedia
The presence of chronic heart failure (CHF) results in a significant risk of leg oedema. Medical compression (MC) treatment is one of the basic methods of leg oedema elimination in… Click to show full abstract
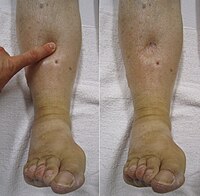
The presence of chronic heart failure (CHF) results in a significant risk of leg oedema. Medical compression (MC) treatment is one of the basic methods of leg oedema elimination in patients with chronic venous disease and lymphedema, but it is not routinely considered in subjects with CHF‐related swelling. In the study, an overview of the current knowledge related to the benefits and risk of using MC in the supportive treatment of leg oedema in CHF patients is presented. The available studies dedicated the comprehensive management of leg swelling using MC in CHF patients published in the English language literature till December 2019 were evaluated in term of the treatment efficacy and safety. In studies performed on CHF populations, manual lymphatic drainage, MC stocking, multilayer bandaged, as well as intermittent pneumatic compression or electric calf stimulations were used. The current evidence is based on non‐randomized studies, small study cohorts, as well as very heterogenous populations. The use of the intermittent pneumatic compression in CHF patients significantly increases the right auricular pressure and mean pulmonary artery pressures as well as decreases systemic vascular resistance in most patients without the clinical worsening. The transient and rapid increase in the human atrial natriuretic peptide, after an application of the MC stocking in New York Heart Association (NYHA) class II patients was observed without clinical exacerbation. An application of the multilayer bandages in NYHA classes III and IV patients lead a significant increase in the right arterial pressure and lead to transient deterioration of the right and the left ventricular functions. In the manual lymphatic drainage study, aside from expected leg circumference reduction, no clinical worsening was observed. In a pilot study performed in a small cohort of CHF patients, electrical calf stimulation use resulted in a reduction in the lean mass of the legs without cardiac function worsening. The use of local leg compression can be considered stable CHF patients without decompensated heart function for both CHF‐related oedema treatment and for treatment of the concomitant diseases leading to leg swelling occurrence. The use of MC in more severe classes of CHF (NYHA III and IV) should be the subject of future clinical studies to select the safest and most efficient compression method as well as to select the patients who benefit most from this kind of treatment.
Journal Title: ESC Heart Failure
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!