Photo from wikipedia
High-spin nitrosyl-iron centres of the Enemark-Feltham {FeNO}(7) type exist in aqueous solution. Examples include the tentative brown-ring species [Fe(H2O)(5)(NO)](2+) and a tentative Fe-II/edta/NO species formed in the processes for scrubbing… Click to show full abstract
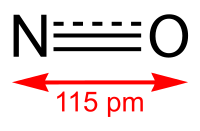
High-spin nitrosyl-iron centres of the Enemark-Feltham {FeNO}(7) type exist in aqueous solution. Examples include the tentative brown-ring species [Fe(H2O)(5)(NO)](2+) and a tentative Fe-II/edta/NO species formed in the processes for scrubbing NO from flue-gas streams. Inert-gas bubbling through the solutions subdivides the ferrous nitrosyl complexes in a less stable subclass - a prominent member being the brown-ring complex - and a more stable subclass to which the edta species belongs. The structural chemistry of the less stable subclass of {FeNO}(7)-type complexes from aqueous media is presented here. They contain aminecarboxylato co-ligands of limited denticity and aqua ligands that complete an OC-6 environment of the Fe atom. Crystalline compounds for single-crystal structure analysis were obtained for various co-ligands: [Fe(H2O)(2)(ida)(NO)] (2a), [Fe(H2O)(heida)(NO)] (2b), [Fe(H2O)(2)(NO)(oda)] (2c), [Fe(H2O)(2)(NO)(phida)]H2O (2d), [Fe(bnida)(H2O)(2)(NO)] (2e), [Fe(brbnida)(H2O)(2)(NO)] (2f) and [Fe(dipic)(H2O)(2)(NO)] (2g) (ida = iminodiacetate, heida = hydroxyethyliminodiacetate, oda = oxodiacetate, phida = N-phenyliminodiacetate, bnida = N-benzyliminodiacetate, brbnida = N-4-bromobenzyliminodiacetate, dipic = dipicolinate). The Fe-NO interaction was studied by DFT and CASSCF methods. Due to mostly covalent Fe-NO bonds, the charge distribution in the less stable subclass is close to Fe-II(NO) with a small Fe-III(NO-) contribution.
Journal Title: European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!