Photo from wikipedia
Light chain amyloidosis is characterized by the progressive deposition of immunoglobulin light chains into the extracellular tissue, leading to organ dysfunction. Usually, it is associated with an underlying clonal plasma… Click to show full abstract
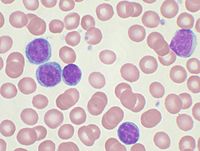
Light chain amyloidosis is characterized by the progressive deposition of immunoglobulin light chains into the extracellular tissue, leading to organ dysfunction. Usually, it is associated with an underlying clonal plasma cell dyscrasia and rarely with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Herein, we described the first report of a patient with relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukaemia harbouring TP53 abnormalities who developed, histologically proven, systemic light chain amyloidosis who was treated with the PI3K inhibitor, idelalisib, and rituximab. Unfortunately, the patient had sudden death during sleep, likely caused by arrhythmia secondary to amyloid cardiomyopathy. Idelalisib was at least effective in reducing secretory free light chain, chronic lymphocytic leukaemia burden, and to improve the survival of patient.
Journal Title: Hematological Oncology
Year Published: 2018
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!