Photo from wikipedia
Skin carcinoma such as melanoma (MM) and cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) are considered as the highest mortality and the most aggressive skin cancers in dermatology. In view that early… Click to show full abstract
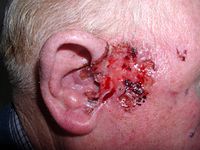
Skin carcinoma such as melanoma (MM) and cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) are considered as the highest mortality and the most aggressive skin cancers in dermatology. In view that early diagnosis and treatment can greatly improve the survival rate and life quality of the patients, developing noninvasive and effective evaluation methods is of great significance for the detection and identification of early stage cutaneous cancers. In this letter, we proposed a hybrid photoacoustic and hyperspectral dual modality microscope (PAHSM) to evaluate and differentiate skin carcinoma by structural and multi physiological parameters. The proposed system's imaging abilities were verified by mimic phantoms and normal mice experiments. Furthermore, in vivo characterization and evaluation results of MM and cSCC mice were obtained successfully, which proved this novel method could be used as a reliable and useful method for skin cancer detection in early stages. This article is protected by copyright. All rights reserved.
Journal Title: Journal of biophotonics
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!