Photo from wikipedia
Hepatotoxicity induced by acetaminophen (APAP)‐overdose is a major concern in clinical practice. In the present work, the detoxifying effect of irbesartan (Irb) on the APAP‐induced acute liver injury was evaluated… Click to show full abstract
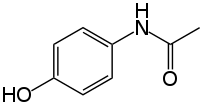
Hepatotoxicity induced by acetaminophen (APAP)‐overdose is a major concern in clinical practice. In the present work, the detoxifying effect of irbesartan (Irb) on the APAP‐induced acute liver injury was evaluated in mice. Induction of acute liver injury in mice was established by a single intraperitoneal (IP) injection of APAP (0.5 g/kg), then mice were injected with Irb (50 or 75 mg/kg, IP), each given twice at 1 and 12 hours post APAP injection. Liver functions, hepatic oxidative and nitrosative stress markers, and liver histopathology were determined after 24 hours. Hepatic cytochrome P450 2E1 (CYP2E1), nuclear factor‐κB (NF‐κB), tumor necrosis factor‐α (TNF‐α), caspase‐3, B‐cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl‐2), and Bcl‐2‐associated X protein (Bax) levels were also estimated. Immunohistochemical evaluations of hepatic expression of phosphorylated NF‐kB and active caspase‐3 were assigned. Irb treatment attenuated APAP‐induced acute liver injury. Irb suppressed APAP‐caused elevation of liver enzymes as well as oxidative and nitrosative stress in liver tissues as evidenced by the decrease in hepatic CYP2E1 expression and hepatic levels of malondialdehyde and nitric oxide in addition to the elevated hepatic superoxide dismutase activity and reduced glutathione concentration. Also, Irb mitigated APAP‐induced inflammation in liver tissues via decreasing the expression of hepatic NF‐κB, phosphorylated NF‐κB and TNF‐α, and attenuated hepatic apoptosis via decreasing Bax/Bcl‐2 ratio and caspase 3 expression and activation. Also, Irb mitigated the APAP‐induced histopathological changes in liver specimens. These data suggested that Irb ameliorates APAP‐induced acute liver injury through antioxidant, anti‐inflammatory, and antiapoptotic activities.
Journal Title: Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!