Photo from wikipedia
We have previously shown that protein kinase Cε (PKCε) is involved in mitochondrial dysfunction in renal proximal tubular cells (RPTC). This study examined mitochondrial targets of active PKCε in RPTC… Click to show full abstract
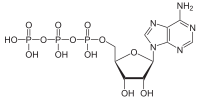
We have previously shown that protein kinase Cε (PKCε) is involved in mitochondrial dysfunction in renal proximal tubular cells (RPTC). This study examined mitochondrial targets of active PKCε in RPTC injured by the model oxidant tert‐butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP). TBHP exposure augmented the levels of phosphorylated (active) PKCε in mitochondria, which suggested translocation of PKCε to mitochondria after oxidant exposure. Oxidant injury decreased state 3 respiration, adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production, ATP content, and complex I activity. Further, TBHP exposure increased ΔΨm and production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and induced mitochondrial fragmentation and RPTC death. PKCε activation by overexpressing constitutively active PKCε exacerbated decreases in state 3 respiration, complex I activity, ATP content, and augmented RPTC death. In contrast, inhibition of PKCε by overexpressing dnPKCε mutant restored state 3 respiration, respiratory control ratio, complex I activity, ΔΨm, and ATP production and content, but did not prevent decreases in F0F1‐ATPase activity. Inhibition of PKCε prevented oxidant‐induced production of ROS and mitochondrial fragmentation, and reduced RPTC death. We conclude that activation of PKCε mediates: (a) oxidant‐induced changes in ΔΨm, decreases in mitochondrial respiration, complex I activity, and ATP content; (b) mitochondrial fragmentation; and (c) RPTC death. In contrast, oxidant‐induced inhibition of F0F1‐ATPase activity is not mediated by PKCε. These results show that, in contrast to the protective effects of PKCε in the heart, PKCε activation is detrimental to mitochondrial function and viability in RPTC and mediates oxidant‐induced injury.
Journal Title: Journal of Cellular Biochemistry
Year Published: 2018
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!