Photo from wikipedia
Safety profiles and humoral responses to inactivated severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‐CoV‐2) vaccines have been previously assessed, but cellular immune responses to inactivated SARS‐CoV‐2 vaccines remain understudied. Here,… Click to show full abstract
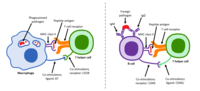
Safety profiles and humoral responses to inactivated severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‐CoV‐2) vaccines have been previously assessed, but cellular immune responses to inactivated SARS‐CoV‐2 vaccines remain understudied. Here, we report the comprehensive characteristics of SARS‐CoV‐2‐specific CD4+ and CD8+ T‐cell responses elicited by the BBIBP‐CorV vaccine. A total of 295 healthy adults were recruited, and SARS‐CoV‐2‐specific T‐cell responses were detected after stimulation with overlapping peptide pools spanning the entire length of the envelope (E), membrane (M), nucleocapsid (N), and spike (S) proteins. Robust and durable CD4+ (p < 0.0001) and CD8+ (p < 0.0001) T‐cell responses specific to SARS‐CoV‐2 were detected following the third vaccination, with an increase in specific CD8+ T‐cells, compared to CD4+ T‐cells. Cytokine profiles showed that interferon gamma and tumor necrosis factor‐α were predominantly expressed with the negligible expression of interleukin (IL)‐4 and IL‐10, indicating a Th1‐ or Tc1‐biased response. Compared to E and M proteins, N and S activated a higher proportion of specific T‐cells with broader functions. The predominant frequency of the N antigen (49/89) was highest for CD4+ T‐cell immunity. Furthermore, N19–36 and N391–408 were identified to contain dominant CD8+ and CD4+ T‐cell epitopes, respectively. In addition, N19–36‐specific CD8+ T‐cells were mainly effector memory CD45RA cells, whereas N391–408‐specific CD4+ T‐cells were mainly effector memory cells. Therefore, this study reports comprehensive features of T‐cell immunity induced by the inactivated SARS‐CoV‐2 vaccine BBIBP‐CorV and proposes highly conserved candidate peptides which may be beneficial in vaccine optimization.
Journal Title: Journal of Medical Virology
Year Published: 2023
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!