Photo from wikipedia
The 94 kDa molecular chaperone, glucose‐regulated protein 94 (Grp94), has garnered interest during the last decade due to its direct association with endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and disease. Grp94 belongs to… Click to show full abstract
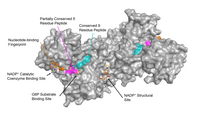
The 94 kDa molecular chaperone, glucose‐regulated protein 94 (Grp94), has garnered interest during the last decade due to its direct association with endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and disease. Grp94 belongs to the Hsp90 family of molecular chaperones and is a master regulator of ER homeostasis due to its ability to fold and stabilize proteins/receptors, and to chaperone misfolded proteins for degradation. Multiple studies have demonstrated that Grp94 knockdown or inhibition leads to the degradation of client protein substrates, which leads to disruption of disease‐dependent signaling pathways. As a result, small molecule inhibitors of Grp94 have become a promising therapeutic approach to target a variety of disease states. Specifically, Grp94 has proven to be a promising target for cancer, glaucoma, immune‐mediated inflammation, and viral infection. Moreover, Grp94‐peptide complexes have been utilized effectively as adjuvants for vaccines against a variety of disease states. This work highlights the significance of Grp94 biology and the development of therapeutics that target this molecular chaperone in multiple disease states.
Journal Title: Medicinal Research Reviews
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!