Photo from wikipedia
INTRODUCTION Congenital pseudarthrosis of the tibia (CPT) is one of the most challenging orthopedic disorders. The use of a vascularized tibial periosteal grafts has been recently reported as a powerful… Click to show full abstract
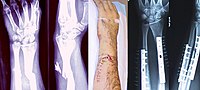
INTRODUCTION Congenital pseudarthrosis of the tibia (CPT) is one of the most challenging orthopedic disorders. The use of a vascularized tibial periosteal grafts has been recently reported as a powerful tool to obtain bone union. We report its use in CPT. PATIENTS AND METHODS Retrospective short-term study of 29 children (18 male/11 female, 15 right-sided/14 left-sided) of mean age 45 months (range 11-144 months), operated upon after October 2014. Nonunion site was debrided, and the periosteum of the involved limb was excised. A vascularized tibial periosteal graft (mean length 10.7 cm (range 9-15 cm) with a monitoring skin island (mean length 4.1 cm (range 3-5 cm) and based on the anterior tibial vessels, was obtained from the contralateral tibia. Anterior tibial vessels were always the recipient vessels. Most cases were stabilized with an LCP plate. The rate of and time to bone union were analyzed. Charts only were evaluated through the first 3 months after bone union was achieved. RESULTS The flap survived and bone union was obtained in all cases, through a periosteal callus, in a mean time of 5.1 weeks (range 3-6 weeks). Mean follow-up was 8.3 months (range 7-19 months). No union failures occurred 3 months after resuming unprotected weight bearing. CONCLUSIONS Our novel technique produced a consistent, rapid capacity for CPT union, superior to previously-reported techniques. However, it cannot be recommended as a standard method of treatment until consistent, long-term, refracture-free follow-up is documented.
Journal Title: Microsurgery
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!