Photo from wikipedia
BACKGROUND In thoracic "outlet" syndrome (TOS), pathologic evidence is well documented for vascular but not neurologic compression. We hypothesized that histologic evidence of compression would be identified at sites where… Click to show full abstract
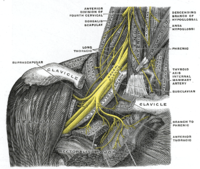
BACKGROUND In thoracic "outlet" syndrome (TOS), pathologic evidence is well documented for vascular but not neurologic compression. We hypothesized that histologic evidence of compression would be identified at sites where the upper trunk was impacted by the anterior scalene muscle and the lower trunk by anatomic anomalies or the first rib. The purpose of this study was to investigate this hypothesis in human cadavers. MATERIALS AND METHODS Twenty-five cadavers' brachial plexuses were dissected and excised. Histologic and descriptive analysis was directed at juncture 1, the upper trunk and anterior scalene muscle, and juncture 2, C8 and T1 nerve roots (lower trunk) with the posterior border of the first rib. Measurements were obtained at the juncture of the T1 nerve root with the C8 nerve root in relationship to the first rib. RESULTS Histologic analysis demonstrated epineurial and perineurial fibrosis, myelin thinning, and Renaut bodies at junctures 1 and 2. Lower trunk formation occurred on or lateral to the first rib in 66% of specimens, with asymmetry in 32% of cadavers. A muscle of Albinus was present in 18% of cadavers. A large dorsal scapular artery coursed through 36% of plexuses with a high, arched subclavian artery. CONCLUSIONS We report histologic changes consistent with chronic compression of the upper and lower plexus in the thoracic inlet at hypothesized sites of brachial plexus compression that may correlate with clinical neck/shoulder (upper trunk) and "ulnar nerve-like" (C8-T1/lower trunk) symptoms. Anatomic anomalies identified should alert the surgeon to variations of lower trunk formation at compression sites.
Journal Title: Microsurgery
Year Published: 2023
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!