Photo from wikipedia
Concomitant lower neonatal brachial plexus palsy (Klumpke) and spinal cord injury is extremely rare but with a clearly established mechanism of injury pattern. No successful surgical techniques have been reported… Click to show full abstract
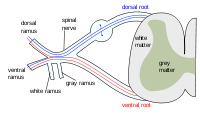
Concomitant lower neonatal brachial plexus palsy (Klumpke) and spinal cord injury is extremely rare but with a clearly established mechanism of injury pattern. No successful surgical techniques have been reported to date to restore intrinsic hand function. We report a case of successful transfer of the extensor carpi radialis brevis motor branch to the deep branch of the ulnar nerve to repair intrinsic hand palsy. Three-month-old boy with the diagnosis of left Klumpke paralysis and thoracic spinal cord injury associating left Horner's sign, intrinsic minus deformity of all the digits, and thenar muscle paralysis in the upper limb. Both lower limbs were fully paralyzed. Cervical magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed spinal cord narrowing from T1 to T5 and pseudo-meningoceles involving the left C8 through T3 roots. Since no spontaneous recovery was apparent by 6.5 months and surgical exploration showed pronator quadratus denervation, the ECRB motor branch deep branch was transferred to the ulnar nerve (DBUN) with interposed a 7.5 cm-long sural nerve graft. By 18 months post-operatively, all the digits showed complete active IP extension. Thirty-six months after surgery, no signs of first dorsal interosseous nerve or thenar muscle reinnervation were present, thus an extensor carpi ulnaris opponensplasty was performed. ECRB motor branch might be a valuable tool to restore finger intrinsic function in these uncommon cases.
Journal Title: Microsurgery
Year Published: 2023
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!