Photo from wikipedia
Despite the considerable research efforts invested over the years to measure the fitness costs of herbicide resistance, these have rarely been used to inform a predictive theory about the fate… Click to show full abstract
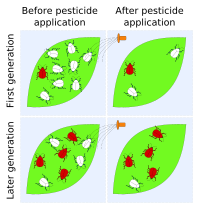
Despite the considerable research efforts invested over the years to measure the fitness costs of herbicide resistance, these have rarely been used to inform a predictive theory about the fate of resistance once the herbicide is discontinued. One reason for this may be the reductive focus on relative fitness of two genotypes as a single measure of differential performance. Although the extent of variation in relative fitness between resistant and susceptible plants has not been assessed consistently, we know enough about plant physiology and ecology not to reduce it to a single fixed value. Research must therefore consider carefully the relevance of the experimental environment, the life stage and the choice of metric when measuring fitness-related traits. The reason most often given for measuring the cost of resistance, prediction of the impacts of management options on population dynamics, cannot be addressed using arbitrary components of fitness or a fixed value of relative fitness. To inform management options, the measurement of traits that capture the relevant processes and the main causes of their variation are required. With an emphasis on the benefit of field experiments measured over multiple time points and seasons, we highlight examples of studies that have made significant advances in this direction. © 2017 Society of Chemical Industry.
Journal Title: Pest management science
Year Published: 2018
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!