Photo from wikipedia
Antimicrobial materials with immobilized particles are of considerable interest. Sulfur, as one of the abundant elements on earth, is cheap and environmentally friendly; therefore, sulfur particles (SPs) can be used… Click to show full abstract
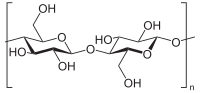
Antimicrobial materials with immobilized particles are of considerable interest. Sulfur, as one of the abundant elements on earth, is cheap and environmentally friendly; therefore, sulfur particles (SPs) can be used as an effective, nontoxic and low‐cost alternative to metal particles. SPs were prepared by precipitation method using sodium thiosulfate and hydrochloric acid in the presence of chitosan as a stabilizer. Further, SPs were grafted on polyethylene terephthalate (PET) foil activated by ultraviolet radiation. The changes in surface properties of modified foils were characterized by contact angle measurement, electrokinetic analysis and X‐ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The contact angle decreased on the UV‐treated sample, owing to the formation of oxidized groups. The presence of nitrogen and sulfur on the polymer surface, revealed by XPS, showed that chitosan‐capped SPs were bound to this surface. The surface morphology of samples and particle sizes were examined by scanning electron microscopy. The size of SPs increased after grafting on surface to a few micrometres. The antibacterial activity of the PET samples was tested against Staphylococcus epidermidis and Escherichia coli bacteria strains. UV‐treated samples grafted with one of the tested chitosan‐capped SPs demonstrated antibacterial effect against both of the bacteria strains. This new nanocomposite has potential to be used in medical applications as an antibacterial agent or in food processing as an antimicrobial food packaging material. Food spoilage caused by microorganisms such as E. coli during distribution and storage has a major impact on food quality and shelf life.
Journal Title: Surface and Interface Analysis
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!