Photo from wikipedia
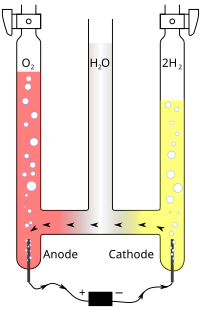
Investigating dendrite-free stripping/plating anodes is highly significant for advancing the practical application of aqueous alkaline batteries. Sn has been identified as a promising candidate for anode material, but its deposition/dissolution… Click to show full abstract
Investigating dendrite-free stripping/plating anodes is highly significant for advancing the practical application of aqueous alkaline batteries. Sn has been identified as a promising candidate for anode material, but its deposition/dissolution efficiency is hindered by the strong electrostatic repulsion between Sn(OH)3 - and the substrate. Herein, this work constructs a nondense copper layer which serves as stannophile and hydrogen evolution inhibitor to adjust the tendency of competing reactions on Sn foil surface, thus achieving a highly reversible Sn anode. The interactions between the deposited Sn and the substrates are also strengthened to prevent shedding. Notably, the ratio of Sn redox reaction is significantly boosted from ≈20% to ≈100%, which results in outstanding cycling stability over 560 h at 10 mA cm-2 . A Sn//Ni(OH)2 battery device is also demonstrated with capacities from 0.94 to 22.4 mA h cm-2 and maximum stability of 1800 cycles.
Journal Title: Small
Year Published: 2023
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!