Photo from wikipedia
The current standard murine model of bone metastasis by using intracardiac injection (IC) has some limitations despite the great utility of this model. This fact emphasizes the need for a… Click to show full abstract
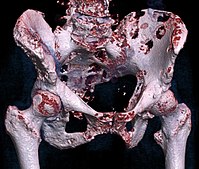
The current standard murine model of bone metastasis by using intracardiac injection (IC) has some limitations despite the great utility of this model. This fact emphasizes the need for a new murine model to accelerate basic research of bone metastasis. The present protocol provides instructions on caudal artery (CA) injection that is an easy-to-use method to reliably construct a murine bone metastasis model with a variety type of cancer cell lines. Bioluminescence imaging visualized that cancer cells injected via the caudal artery in the tail were efficiently delivered to a hind limb bone, where it is a common site affected with bone metastasis in mice. CA injection rarely causes stress-induced acute death in mice and enables us to inject a large number of cancer cells, thereby greatly increasing the frequency of bone metastasis in hind limb bones. Importantly, CA injection is technically as easy as tail vein injection and causes no lethal stress, indicating that it is a model that also contributes to animal welfare. CA injection model, therefore, could represent a powerful tool for many researchers to study molecular mechanisms of bone metastasis in mice.
Journal Title: Methods in molecular biology
Year Published: 2021
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!