Photo from wikipedia
Brain is one of the most energy-demanding organs. Energy in the form of ATP is produced in brain cells predominantly in oxidative phosphorylation coupled to mitochondrial respiration. Any alteration of… Click to show full abstract
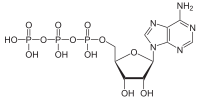
Brain is one of the most energy-demanding organs. Energy in the form of ATP is produced in brain cells predominantly in oxidative phosphorylation coupled to mitochondrial respiration. Any alteration of the mitochondrial metabolism or prolonged ischemic or anoxic conditions can lead to serious neurological conditions, including neurodegenerative disorders. Assessment of mitochondrial metabolism is important for understanding physiological and pathological processes in the brain. Bioenergetics in central nervous system is dependent on multiple parameters including neuron-glia interactions and considering this, in vivo or ex vivo, the measurements of mitochondrial metabolism should also be complimenting the experiments on isolated mitochondria or cell cultures. To assess the mitochondrial function, there are several key bioenergetic parameters which indicate mitochondrial health. One of the major characteristics of mitochondria is the mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) which is used as a proton motive force for ATP production and generated by activity of the electron transport chain. Major donor of electrons for the mitochondrial respiratory chain is NADH. Here we demonstrate how to measure mitochondrial NADH/NAD(P)H autofluorescence and ΔΨm in acute brain slices in a time-dependent manner and provide information for the identification of NADH redox index, mitochondrial NADH pool, and the rate of NADH production in the Krebs cycle. Additionally, non-mitochondrial NADH/NADPH autofluorescence can signify the level of activity of the pentose phosphate pathway.
Journal Title: Methods in molecular biology
Year Published: 2021
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!