Photo from wikipedia
OBJECTIVE Complete olecranon bursectomy with debridement, protection of veins and nerves. Risk-adapted antibiotic therapy and early functional aftercare. INDICATIONS Acute, traumatic laceration of the bursa olecrani, chronic therapy-resistant bursitis olecrani.… Click to show full abstract
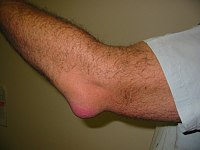
OBJECTIVE Complete olecranon bursectomy with debridement, protection of veins and nerves. Risk-adapted antibiotic therapy and early functional aftercare. INDICATIONS Acute, traumatic laceration of the bursa olecrani, chronic therapy-resistant bursitis olecrani. CONTRAINDICATIONS For traumatic bursa injuries: general contraindications for anesthesia and surgery; chronic bursitis: initially not closable skin defect (plastic surgery required), hemodynamically instable patient (e.g. systemic inflammatory response syndrome [SIRS] or sepsis), pre-existing skin infection. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Local anesthesia beyond the lesion, careful debridement, identification and removal of the entire bursa, excision of contaminated skin, lavage, drain insertion (Redon, Easy-flow, Penrose). Wound closure, elastic bandage, and splint. POSTOPERATIVE MANAGEMENT Elastic bandage for 2 days, followed by drain removal. Wound assessment, early functional aftercare without splint, antibiotic therapy in septic bursitis for 2 weeks, PRICE scheme. Removal of stitches after 10-12 days. RESULTS Over 5 years, 138 cases of traumatic bursa lesion or chronic bursitis olecrani were treated in our clinic, 82 patients underwent surgery. Ten patients were treated with vacuum-assisted closure therapy and consecutive wound healing; fistulae occurred in two patients and in another two dehiscence developed. All of the defects could be closed without flaps.
Journal Title: Operative Orthopadie und Traumatologie
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!