Photo from wikipedia
OBJECTIVE Reconstruction of proximal humeral bone defects in the setting of shoulder revision arthroplasty by implantation of a modular humeral component. INDICATIONS Severe segmental humeral bone defects in revision total shoulder… Click to show full abstract
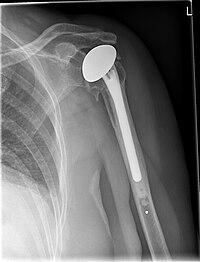
OBJECTIVE Reconstruction of proximal humeral bone defects in the setting of shoulder revision arthroplasty by implantation of a modular humeral component. INDICATIONS Severe segmental humeral bone defects in revision total shoulder arthroplasty, after tumor resection, trauma, pathological fractures, post-infectious or after failed osteosynthesis. CONTRAINDICATIONS Acute or chronic local infections, large diaphyseal bone defects preventing adequate anchorage of the prosthesis, very short life expectancy (<3 months). SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Removal of the implant using an extended deltopectoral approach. Periarticular arthrolysis with preservation of neurovascular structures. Resection of the meta-diaphyseal bone and reconstruction of the humeral length with the help of different extension sleeves and a modular humeral component. Soft tissue management is crucial, especially with reverse shoulder arthroplasty. POSTOPERATIVE MANAGEMENT Three weeks postoperatively immobilization in a shoulder sling, active assisted movement therapy by gradual pain-adapted increase of movement, muscle coordination, and strength. RESULTS The results of 11 consecutive patients treated with a modular humeral component due to a failed shoulder arthroplasty between 2008 and 2016 were evaluated retrospectively. Mean length of reconstruction was 100 mm. Due to recurrent dislocations one patient required revision and conversion to a reverse component. No cases of aseptic loosening or periprosthetic infection were observed.
Journal Title: Operative Orthopadie und Traumatologie
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!