Photo from wikipedia
Dear Editor, Patients with a treated cerebral aneurysm require follow-up to evaluate the level of aneurysm occlusion, or poss ible recanal iza t ion. In the fol low-up of endovascular… Click to show full abstract
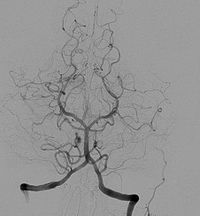
Dear Editor, Patients with a treated cerebral aneurysm require follow-up to evaluate the level of aneurysm occlusion, or poss ible recanal iza t ion. In the fol low-up of endovascular coil embolization–treated aneurysms, MR angiography is the preferred imaging modality because of its high diagnostic accuracy with only limited artifacts from the coils [1]. MR angiography has a clear advantage over digital subtraction angiography (DSA) because it is a non-invasive procedure and does not necessarily require administration of a contrast agent. However, some patients cannot undergo an MRI examination due to unsafe implants (e.g., a pacemaker) or because of claustrophobia. MR angiography is also not feasible in patients with an aneurysm treated with a surgical clip, flow diverter, or WEB (Woven EndoBridge) device, due to susceptibility artifacts hampering the diagnostic evaluation. In these situations, DSA is routinely performed in the follow-up of treated cerebral aneurysms. DSA is an expensive, time-consuming, and invasive procedure with a small, but non-negligible risk of complications [2]. A non-invasive imaging modality is therefore preferred. Recent developments in CT software and hardware, such as metal artifact reduction (MAR), advanced image registration and subtraction techniques, and high spatial resolution CT scanners, are now available for application in clinical practice, resulting in superior image quality with only limited artifacts from the implanted materials [3–5]. This is illustrated by two cases we recently encountered in our hospital, where subtraction CT angiography (CTA) with MAR and DSA was performed (Fig. 1). In the first case, recanalization of a WEB devicetreated aneurysm of the anterior communication artery was clearly seen on high-resolution subtraction CTA and confirmed by DSA. In the second case, high-resolution subtraction CTA was performed in the follow-up of an anterior communicating artery aneurysm treated with coil embolization demonstrating full occlusion of the aneurysm. MR angiography was not possible in this case due to an MRI unsafe pacemaker, and DSA was not preferred because of comorbidity. Both patients were scanned on a 160-row multi-detector system (Aquilion Precision, Canon Medical Systems, Otawara, Japan) resulting in a spatial resolution of 0.234 mm (1024 × 1024 matrix, 0.4 × 0.5-mm focus size, 0.35-s gantry rotation time, 120 kV, 150 mAs). A bolus of 50-mL contrast agent (Iomeron 300) was used. The diagnostic accuracy of subtraction CTA as compared withDSA in the follow-up of treated cerebral aneurysms still needs to be evaluated in prospective cohort studies. For a reliable comparison, it is crucial that subtraction CTA and DSA are performed at the same moment during follow-up; however, they need to be evaluated independently by observers blinded to the reference standard. The type of aneurismal closure device should be taken into account. Preliminary results of flow diverter–treated aneurysms suggest that the diagnostic accuracy of subtraction CTA at conventional spatial resolution seems comparablewithDSA [3]. The addedvalueof subtractionCTAat high spatial resolution also needs to be evaluated, though initial results demonstrate superior image quality at a comparable radiation dose [4]. * Frederick J. A. Meijer [email protected]
Journal Title: Neuroradiology
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!