Photo from wikipedia
Intracranial aneurysms (IA) in children are rare, accounting for less than 5% of all IA. Due to their scarcity, the epidemiology is poorly understood and differs from adults in term… Click to show full abstract
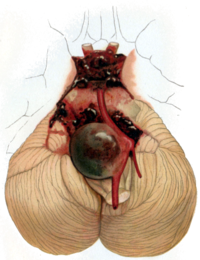
Intracranial aneurysms (IA) in children are rare, accounting for less than 5% of all IA. Due to their scarcity, the epidemiology is poorly understood and differs from adults in term of clinical presentation, size, location, and origin. Consequently, the treatment strategies are specific and cannot be only based on data from adult series. The aim of our study was to report the characteristics, management, and outcomes of children treated for IA in two university hospitals located in Normandy (France) over the last 17 years and to perform a literature review of this rare pathology. This retrospective study included 18 consecutive children (< 18 years old) admitted with cerebral aneurysm treated in two neurosurgery departments in Normandy, from 2001 to 2018. Computerized tomography and cerebral angiography established the diagnosis. Both endovascular and surgical procedures were discussed in all cases. Data focused on clinical condition at admission, characteristics of the IA, choice of the treatment modalities, and complications. The outcome at follow-up is based on Glasgow outcomes scale (GOS) at 1 year. During the study period, 18 children (mean age: 12.6 years; sex ratio male/female: 2.3) were admitted with 21 IA. Aneurysms had a mean size of 13.6 mm with 4 giant aneurysms and were mostly located in the anterior circulation (16/21). Clinical presentations at onset were sudden symptoms related to a subarachnoid hemorrhage in 13 patients, headaches in 4 patients with giant aneurysm, and asymptomatic in one patient. Among the 13 patients with ruptured IA, 6 presented in poor preoperative condition (Hunt and Hess Grade ≥ 4). Treatment modalities consisted in embolization in 9 patients and surgery in 9 patients including 2 by-pass surgeries in fusiform aneurysms. Complications were similar in the two groups, but two cases of recanalization were observed in the endovascular group. At 1 year of follow-up, 14 children were in good condition (GOS Score > 4) and one died. Three children presented associated IA treated by the same technique as initial aneurysm. Pediatric aneurysm is a different pathology compared with adults, occurring more frequently in male population with a higher proportion of giant aneurysms and aneurysms located in the internal carotid bifurcation. The use of endovascular techniques has progressed in the last years, but surgery was proposed for half of our population.
Journal Title: Child's Nervous System
Year Published: 2021
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!