Photo from wikipedia
Background Despite the well-known second trimester ultrasound signs, current possibilities of in utero surgical repair of open spina bifida require a timely detection of the spine defect. Objective To evaluate… Click to show full abstract
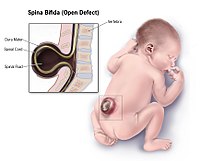
Background Despite the well-known second trimester ultrasound signs, current possibilities of in utero surgical repair of open spina bifida require a timely detection of the spine defect. Objective To evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of the ratio between brain stem (BS) diameter and its distance to the occipital bone (BSOB) (BS/BSOB ratio) in the detection of fetuses with open spina bifida at first trimester ultrasound. Methods A systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy was performed by searching seven electronic databases from their inception to February 2019 for all studies assessing the association between BS/BSOB ratio and diagnosis of spine bifida . Diagnostic accuracy of BS/BSOB ratio in prenatal diagnosis of spine bifida was assessed as sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative likelihood ratios (LR + and LR−), and area under the curve (AUC) on SROC curves. Results Four studies, including 17,598 fetuses with 23 cases of open spina bifida, were included in the meta-analysis. BS/BSOB ratio showed pooled sensitivity of 0.70 (95% CI 0.47–0.87; I 2 = 78.3%), specificity of 1.00 (95% CI 0.99–1.0; I 2 = 99.2%), LR + and LR− of 51.44 (95% CI 9.53–277.64; I 2 = 85.5%) and 0.23 (95% CI 0.04–1.17; I 2 = 64.8%), respectively, and an AUC of 0.9649. Conclusion First trimester BS/BSOB ratio has a high diagnostic accuracy in detecting fetuses with open spina bifida.
Journal Title: Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!