Photo from wikipedia
The aim of the present article is to propose an alternative technique to the traditional secondary tracheoesophageal puncture (TEP) for voice rehabilitation after total laryngectomy, describing the procedure step-by-step, analyzing… Click to show full abstract
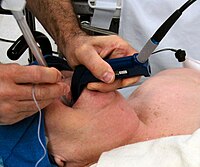
The aim of the present article is to propose an alternative technique to the traditional secondary tracheoesophageal puncture (TEP) for voice rehabilitation after total laryngectomy, describing the procedure step-by-step, analyzing the complications and long-term results. A retrospective study was conducted on patients who underwent secondary TEP with the blind technique using a rigid hysterometer. The main steps in this technique are described and illustrated. Patient demographics and surgical outcomes were assessed. Thirty-two patients were enrolled in this study. In all but one case, risk factors that could hinder rigid esophagoscopy were identified (37.5% neopharyngeal/esophageal post-surgical issues, 81.3% prior radiotherapy, 21.9% cervical arthrosis, and 12.5% prior coloplasty or gastric transposition). No intra- or postoperative surgical complications were noted. The blind technique offers an alternative method to perform a secondary TEP safely and efficiently in patients with unfavorable anatomical or clinical conditions, lowering the risk of procedure-related complications.
Journal Title: European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology
Year Published: 2021
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!