Photo from wikipedia
Background This paper aimed to elucidate the etiologies of all primary ileostomy site malignancies published in the literature. Methods A review of the literature was conducted following PRISMA guidelines by… Click to show full abstract
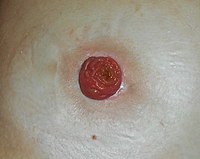
Background This paper aimed to elucidate the etiologies of all primary ileostomy site malignancies published in the literature. Methods A review of the literature was conducted following PRISMA guidelines by querying PubMed, Global Health, and Web of Science for articles published before November 2020. Search criteria contained broad terminology for ileostomy site neoplasms without language, date, or publication limitations. A full-text review of the abstracts confirmed primary malignant pathologies and was evaluated for study inclusion. Results Literature search discovered 858 publications, with 76 meeting eligibility criteria. The final sample contained 91 patients, with equal males and females. The mean age of patients with ileostomy site malignancy was 62.0 ± 12.2, with an average ileostomy age of 29.4 ± 12.4. The most common indications for ileostomy creation were inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) (73.6%) and familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) (20.9%). There was a total of eight ileostomy malignant pathologies reported, with adenocarcinoma being the most common (76.9%), followed by squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) (11.0%). Adenocarcinoma was diagnosed at a younger age than SCC (59.7 vs. 72.3) and developed over a shorter time (28.8 vs. 37.0). Patients with FAP almost exclusively developed adenocarcinoma (94.4%) at a younger stoma age (25.8 vs. 31.4) than those with IBD who developed seven diverse pathologies. With a median follow-up of 0.75 years, four patients developed disease recurrence and received oncologic resection of their cancer less often than the 55 negative patients ( p = 0.04). Conclusion Ileostomy site malignancies are late-appearing complications that require curative surgery. Their presentation is associated with ileostomy duration and creation indication, such as FAP or IBD. We recommend screening at a stoma age ≥ 20 or patient age ≥ 50 for patients with FAP, while stoma age ≥ 25 or patient age ≥ 60 for IBD patients.
Journal Title: Surgical Endoscopy
Year Published: 2022
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!