Photo from wikipedia
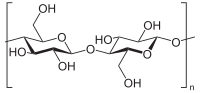
Assembling 1D cellulose nanocrystal into robust functional 3D macro-materials can be conducive to the broad application of nanocomposites, but it remains a huge challenge. Inspired by mussel-like adhesion and nacre… Click to show full abstract
Assembling 1D cellulose nanocrystal into robust functional 3D macro-materials can be conducive to the broad application of nanocomposites, but it remains a huge challenge. Inspired by mussel-like adhesion and nacre structures, functionalized sodium alginate was in-situ synthesized with dopamine as a reinforcement agent and an interface jointer for the cellulose nanocrystal (CNC) nanocomposites with excellent mechanical properties. A rhodamine derivative was developed as a structural modifier to extend bulk strength as well as generate outstanding fluorescence. Through facile vacuum-assisted assembly, the resulting nanocomposites showed 210% and 220% increase in strength and Young’s modulus respectively, without losing ductility. Such experiment results were much higher than those of the reported. The thermal stability and water resistance were also improved remarkably, with favorable fluorescent and photothermal conversion functionalities. This study explored a promising approach to prepare biomimetic CNC nanocomposites with favorable properties and extra functionality, showing great potentials for various applications in fluorescent probe field.
Journal Title: Cellulose
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!