Photo from wikipedia
With the advancements in sensor applications, wireless sensor networks (WSNs) become significant area of research. WSNs compose various tiny sensor nodes to sense an environment, depends upon the given application.… Click to show full abstract
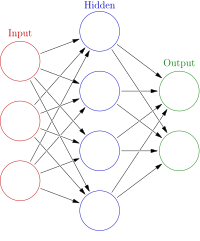
With the advancements in sensor applications, wireless sensor networks (WSNs) become significant area of research. WSNs compose various tiny sensor nodes to sense an environment, depends upon the given application. However, these nodes are battery constrained (i.e., may become dead after passing certain iterations). Therefore, number of energy efficient protocols have been implemented in literature. However, selecting an optimal path between base station and sensor nodes is defined as an ill-posed problem. To overcome this issue, a Deep Q-routing based inter-cluster data aggregation is considered to improve the inter-cluster communication in WSNs. In every epoch, Recurrent neural network is considered to compute shortest path between cluster heads and sink. We have trained the network in such a way that it considers various features of WSNs and able to decide which sensor node will be selected as next-hop to establish a shortest path between elected cluster heads and sink. The non-cluster head nodes may also be considered while selecting a shortest path. Extensive experimental results show that the proposed technique outperforms the competitive energy efficient protocols.
Journal Title: Cluster Computing
Year Published: 2020
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!