Photo from wikipedia
This paper investigated the effects of p-coumaric acid (CA) on stilbene biosynthesis in healthy cuttings of grapevine Vitis amurensis Rupr. under control conditions and after ultraviolet (UV-C) irradiation. It has… Click to show full abstract
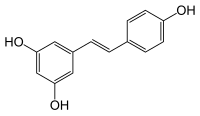
This paper investigated the effects of p-coumaric acid (CA) on stilbene biosynthesis in healthy cuttings of grapevine Vitis amurensis Rupr. under control conditions and after ultraviolet (UV-C) irradiation. It has been shown that the content of the detected six stilbenes (cis-piceid, t-piceid, t-ε-viniferin, cis-ε-viniferin, t-resveratrol, and t-δ-viniferin) increased after feeding with CA up to 0.5 mg g−1 of the dry weight (DW), which is 2.4 times higher than that under control conditions. Feeding with CA and UV-C irradiation exerted a combined positive effect on the content of stilbenes increasing it to 0.7 mg g−1 DW. In addition, the CA treatment improved viability of the cuttings after the UV-C treatment. The elevation in stilbene content induced by CA and UV-C correlated with induction of stilbene biosynthetic genes encoding stilbene synthases, resveratrol O-glucosyltransferase, polyphenol oxidase, and cationic peroxidase. The data indicate that feeding with the precursors of phenolic compounds could be an effective strategy for activation of stilbene production.
Journal Title: Acta Physiologiae Plantarum
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!