Photo from wikipedia
Edge reflections are inevitable in numerical modeling of seismic wavefields, and they are usually attenuated by absorbing boundary conditions. However, the commonly used perfectly matched layer (PML) boundary condition requires… Click to show full abstract
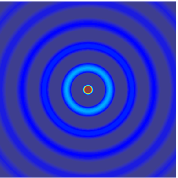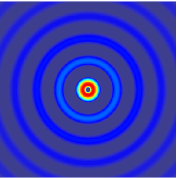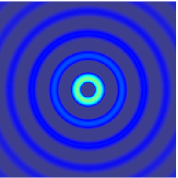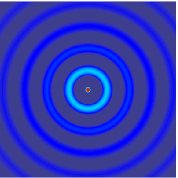
Edge reflections are inevitable in numerical modeling of seismic wavefields, and they are usually attenuated by absorbing boundary conditions. However, the commonly used perfectly matched layer (PML) boundary condition requires special treatment for the absorbing zone, and in three-dimensional (3D) modeling, it has to split each variable into three corresponding variables, which increases the computing time and memory storage. In contrast, the hybrid absorbing boundary condition (HABC) has the advantages such as ease of implementation, less computation time, and near-perfect absorption; it is thus able to enhance the computational efficiency of 3D elastic wave modeling. In this study, a HABC is developed from two-dimensional (2D) modeling into 3D modeling based on the 1st Higdon one way wave equations, and a HABC is proposed that is suitable for a 3D elastic wave numerical simulation. Numerical simulation results for a homogenous model and a complex model indicate that the proposed HABC method is more effective and has better absorption than the traditional PML method.
Journal Title: Applied Geophysics
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!