Photo from wikipedia
Groundwater constitutes an important natural resource in Kuwait and thus requires effective management policies based on a sound knowledge of its flow, recharge, and factors affecting the quality of the… Click to show full abstract
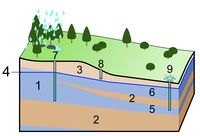
Groundwater constitutes an important natural resource in Kuwait and thus requires effective management policies based on a sound knowledge of its flow, recharge, and factors affecting the quality of the water. An assessment of the flow and water quality changes of the southern Kuwait groundwaters over the past decades was made based on the available hydrogeological, hydrochemical, pumping and tracer tests, and environmental isotopes data. The predevelopment potentiometric surface of the Dammam aquifer was higher than that of the Kuwait Group aquifer. The Dammam groundwater is old and no recharge occurred in Kuwait during pre-development times. The Kuwait Group aquifer was recharged mainly by an upward leakage from the Dammam aquifer, with local recharge largely restricted to the Dibdibba depressions. The continuous groundwater pumping has resulted in the reversal of flow direction. The salinity of the Dammam aquifer at Al-Shegaya and Umm-Gudair has been relatively stable since 1960, whereas the Kuwait Group aquifer has a stable to freshening trend.
Journal Title: Arabian Journal of Geosciences
Year Published: 2018
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!