Photo from wikipedia
The fifth-generation (5G) wireless communication systems associating with the high achievable data-transfer speeds will significantly affect the performance of IoT networks. On one hand, the internet goes through a dramatic… Click to show full abstract
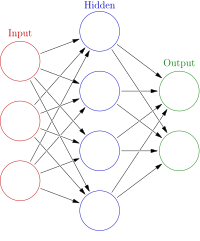
The fifth-generation (5G) wireless communication systems associating with the high achievable data-transfer speeds will significantly affect the performance of IoT networks. On one hand, the internet goes through a dramatic transaction period that shapes every aspect of our lives, industry, and business where cloud computing, smart cities, and the Internet of Things (IoT) play a significant role in the advancement of data transfer, storing, and processing. On the other hand, it plays a significant role in emerging advanced versions of different types of cybersecurity attacks especially that are novel, hard-to-detect, and that of distributive never cease-fire characteristics. To mitigate these concerns, we present a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) intrusion detection model that can be implemented in IoT dynamic environments, providing an intelligent intrusion detection mechanism against the second biggest threat to data traffic and transfer on IoT networks. Kalman backpropagation neural network-based DDoS intrusion detection is proposed in this work. The framework is validated through various simulations via the most up to date CICDDoS2019 dataset to demonstrate the effectiveness of the solution in terms of intrusion detection. the proposed solution achieved an average detection accuracy of 94% with 0.0952 false alarm rate and 97.49%, 91.22% for detection rate, and precision respectively.
Journal Title: International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics
Year Published: 2021
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!