Photo from wikipedia
Presently plastics are major contributors in solid waste which has higher thermal energy. Waste plastics can be converted into alternate fuel by pyrolysis which can replace diesel in compression ignition… Click to show full abstract
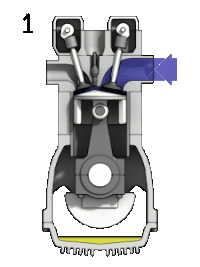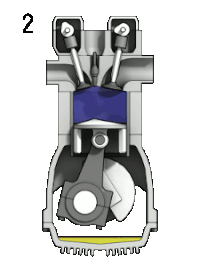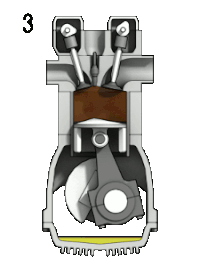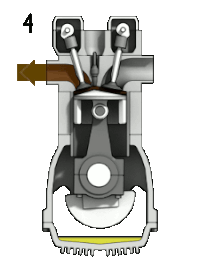
Presently plastics are major contributors in solid waste which has higher thermal energy. Waste plastics can be converted into alternate fuel by pyrolysis which can replace diesel in compression ignition engines. The present study deals with the performance, combustion and emission characteristics of variable compression ratio engine fuelled with plastic oil, diesel and its blends with diethyl ether as an additive. Three blends 2.5, 7.5 and 12.5 % were tested in variable compression ratio engine. Waste plastic oil blend, pure plastic oil and diesel were considered for comparison. This study reveals that brake thermal efficiency increases for all the blends when compression ratio increases from 12 to 20. The specific fuel consumption of the blends and plastic oil were higher than the diesel. But the brake thermal efficiency for all the blends, plastic oil was comparatively lower than that of diesel. The regulated emissions of the variable compression ratio engine under varying loads and compression ratio for different blends were discussed.
Journal Title: Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!