Photo from wikipedia
The design of novel herpes simplex type I (HSV-1)–derived oncolytic virotherapies is a balancing act between safety, immunogenicity, and replicative potential. We have undertaken this review to better understand how… Click to show full abstract
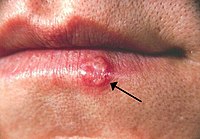
The design of novel herpes simplex type I (HSV-1)–derived oncolytic virotherapies is a balancing act between safety, immunogenicity, and replicative potential. We have undertaken this review to better understand how these considerations can be incorporated into rational approaches to the design of novel herpesvirus oncolytic virotherapies. Several recent papers have demonstrated that enhancing the potential of HSV-1 oncolytic viruses to combat anti-viral mechanisms present in the tumor microenvironment leads to greater efficacy than their parental viruses. It is not entirely clear how the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment affects oncolytic viral replication and spread within tumors. Recent work has shown that the manipulation of specific cellular and molecular mechanisms of immunosuppression operating within the tumor microenvironment can enhance the efficacy of oncolytic virotherapy. We anticipate that future work will integrate greater knowledge of immunosuppression in tumor microenvironments with design of oncolytic virotherapies.
Journal Title: Current Clinical Microbiology Reports
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!