Photo from wikipedia
The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway (UPP) is a major venue for controlled intracellular protein degradation in Eukaryota. The machinery of several hundred proteins is involved in recognizing, tagging, transporting, and cleaving proteins,… Click to show full abstract
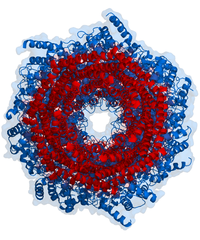
The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway (UPP) is a major venue for controlled intracellular protein degradation in Eukaryota. The machinery of several hundred proteins is involved in recognizing, tagging, transporting, and cleaving proteins, all in a highly regulated manner. Short-lived transcription factors, misfolded translation products, stress-damaged polypeptides, or worn-out long-lived proteins, all can be found among the substrates of UPP. Carefully choreographed protein-protein interactions (PPI) are involved in each step of the pathway. For many of the steps small-molecule inhibitors have been identified and often they directly or indirectly target PPI. The inhibitors may destabilize intracellular proteostasis and trigger apoptosis. So far this is the most explored option used as an anticancer strategy. Alternatively, substrate-specific polyubiquitination may be regulated for a precise intervention aimed at a particular metabolic pathway. This very attractive opportunity is moving close to clinical application. The best known drug target in UPP is the proteasome: the end point of the journey of a protein destined for degradation. The proteasome alone is a perfect object to study the mechanisms and roles of PPI on many levels. This giant protease is built from multisubunit modules and additionally utilizes a service from transient protein ligands, for example, delivering substrates. An elaborate set of PPI within the highest-order proteasome assembly is involved in substrate recognition and processing. Below we will outline PPI involved in the UPP and discuss the growing prospects for their utilization in pharmacological interventions.
Journal Title: Advances in protein chemistry and structural biology
Year Published: 2018
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!