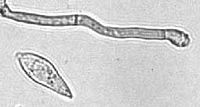
Photo from wikipedia
Abstract CONTEXT Rice blast manifests with different symptoms according to the affected plant organ, i.e., leaf and panicle blast, the latter being the primary determinant of yield losses in Italy.… Click to show full abstract
Abstract CONTEXT Rice blast manifests with different symptoms according to the affected plant organ, i.e., leaf and panicle blast, the latter being the primary determinant of yield losses in Italy. Forecasting models have been developed to drive fungicides application and perform scenario analyses to plan legislative measures on plant protection. An assessment of the blast pathogen pressure evolution in the Italian rice area under climate change realizations has not been done yet. OBJECTIVE We developed the ELLE process-based forecasting model (ricE bLast simuLation modEl) to reproduce the dynamics of leaf and panicle blast severity and incidence to release a tool to perform in-season monitoring and scenario assessment. The forecasting model is delivered as a RESTful API and is ready to be used by third parties for operational monitoring activities. Here we present its application to assess future rice blast impacts in Italy after an extended calibration and evaluation with ground-truth data. METHODS The reference dataset for model testing comprised (a) a multi-year (2013–2015) and multi-site (three locations) experimental trial, where leaf and panicle blast were assessed on four Italian rice varieties with different levels of susceptibility to blast disease, and (b) historical disease data collected at the municipality level. We then performed spatially distributed simulations at 2 × 2 km resolution on the Northern Italian rice district, considering a short- (2030) and long- (2070) term time horizon and rice varieties representative of the current variability in phenology and susceptibility to blast disease within the Italian varietal landscape. The factorial combinations of climatic projections from four General Circulation Models and two extreme CO2 Representative Concentration Pathways were used as model inputs in the scenario analysis. RESULTS AND CONCLUSIONS Model calibration and evaluation at the field level denoted an overall accurate reproduction of leaf blast severity (RRMSE SIGNIFICANCE Besides delivering a reusable methodology to analyze the severity and incidence of leaf and panicle blast, our modelling study confirms that varietal susceptibility is the main feature to be pursued in rice breeding programs to counteract blast disease.
Journal Title: Agricultural Systems
Year Published: 2021
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!