Photo from wikipedia
Background: Patients presenting to the emergency department (ED) with altered mental status and alcohol intoxication can clinically resemble patients with an intracranial hemorrhage. Although intracranial hemorrhage is quickly excluded with… Click to show full abstract
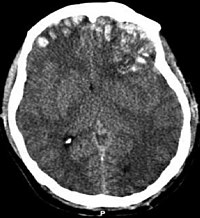
Background: Patients presenting to the emergency department (ED) with altered mental status and alcohol intoxication can clinically resemble patients with an intracranial hemorrhage. Although intracranial hemorrhage is quickly excluded with a head computed tomographic (CT) scan, it is common practice to defer imaging and allow the patient to metabolize to spare ED resources and minimize radiation exposure to the patient. Although this reduces unnecessary scans, it may delay treatment in patients with occult intracranial hemorrhage, which some fear may increase morbidity and mortality. We sought to evaluate the safety of deferred CT imaging in these patients by evaluating whether time to scan significantly affects the rate of neurosurgical intervention. Methods: In this retrospective medical record review, all clinically alcohol‐intoxicated patients presenting to 2 university EDs were included. Time to order CT imaging, findings on imaging, and outcomes of these patients were determined. Patients were assessed in 3 groups: CT ordered within 1 hour of triage, CT ordered 1‐3 hours from triage, and CT ordered 3 or more hours from triage. Results: During the study period, 5943 patients were included in the study. Of these, 0 patients scanned in less than 3 hours had intracranial findings on imaging requiring neurosurgery, whereas 1 patient with a deferred CT scan required a neurosurgical intervention; however, it was not emergently performed. Conclusion: Routine CT scanning of alcohol‐intoxicated patients with altered mental status is of low clinical value. Deferring CT imaging while monitoring improving clinical status appears to be a safe practice.
Journal Title: American Journal of Emergency Medicine
Year Published: 2017
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!