Photo from wikipedia
Abstract In this work, cooling effectiveness decline during operation of cooling towers has been modeled using local linear wavelet neural networks. The algorithm of particle swarm optimization (PSO) is employed… Click to show full abstract
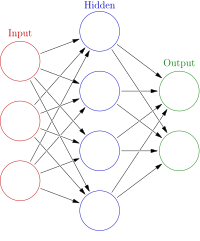
Abstract In this work, cooling effectiveness decline during operation of cooling towers has been modeled using local linear wavelet neural networks. The algorithm of particle swarm optimization (PSO) is employed to optimize the parameters of constructed model. Operating parameters including the dry bulb temperature, humidity ratio of the air stream at the inlet of the tower, the temperature of the inlet water, water-air mass flow rate ratio were considered as the model inputs to predict the outlet water temperature. The proposed hybrid model was validated using experimental data not involved in the training stage. The simulation results show that the ANN-PSO method model is consistent with the real cooling performance of the actual equipment during the fouling process, which solves the problem of complicated calculation and empiricism in conventional methods. It was found that the average relative error ( MRE ) for PSO is 1.17%, the root mean square error ( RMSE ) is 0.6113 °C, and the correlation coefficient is 0.9969. The effect of fouling on the performance of the cooling tower is also demonstrated. It is suggested that the ANN-PSO is an effective and powerful tool for predicting fouling process of a cooling tower.
Journal Title: Applied Thermal Engineering
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!