Photo from wikipedia
Abstract Supercritical CO2 (SCO2) as a working fluid can significantly reduce the compression work in a Brayton power cycle, especially when inlet conditions of the main compressors are set near… Click to show full abstract
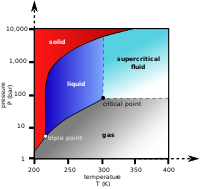
Abstract Supercritical CO2 (SCO2) as a working fluid can significantly reduce the compression work in a Brayton power cycle, especially when inlet conditions of the main compressors are set near the critical point of the CO2. However, near the critical point, the dramatic variation of the physical properties and the potential phase transformation bring about difficulties in achieving converged and accurate numerical simulations of SCO2 compressors. In this paper, a numerical strategy based on commercial density-based computational fluid dynamics (CFD) solver is adopted to model a SCO2 compressor working near the critical point and is validated against experimental data. The effect of property tables with different functions on the accuracy and stability of the numerical simulation is analyzed and discussed in detail. A new sampling method, named quasi-symmetric sampling, is proposed to improve the numerical stability, and proves to be effective in improving the stability of the numerical simulation with little effect on the numerical result.
Journal Title: Applied Thermal Engineering
Year Published: 2021
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!