Photo from wikipedia
Abstract This paper presents a comparison between four modern heuristic algorithms for optimal loss reduction of power distribution network equipped with renewable energy resources. These algorithms are Gravitational Search Algorithm… Click to show full abstract
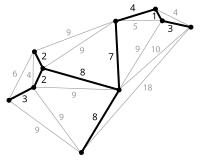
Abstract This paper presents a comparison between four modern heuristic algorithms for optimal loss reduction of power distribution network equipped with renewable energy resources. These algorithms are Gravitational Search Algorithm (GSA), Bat Algorithm (BA), Imperialist Competitive Algorithm (ICA) and Flower Pollination Algorithm (FPA). Placing Renewable Distributed Generators (RDGs) such as wind turbine (WT) and photovoltaic panels (PV) in the electrical grid might share in reducing the power loss. In this research, the proposed heuristic algorithms are utilized to find the optimal location and size of RDGs on the distribution network for the purpose of reducing power loss. A probabilistic optimal load flow technique is implemented to model the behavior of RDGs based on different penetration levels. The proposed algorithms are applied to 69-bus system. The acquired results based on the heuristic algorithms are listed to clarify the effectiveness of the proposed algorithms in reducing the power losses of the studied system.
Journal Title: Ain Shams Engineering Journal
Year Published: 2018
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!