Photo from wikipedia
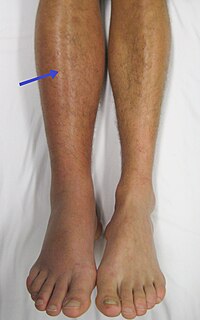
BACKGROUND To develop a diagnostic prediction model to improve identification of acute symptomatic portal vein thrombosis (PVT). METHODS We examined 47 PVT patients and 94 control without PVT in the… Click to show full abstract
BACKGROUND To develop a diagnostic prediction model to improve identification of acute symptomatic portal vein thrombosis (PVT). METHODS We examined 47 PVT patients and 94 control without PVT in the Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University and Suqian People's Hospital of Nanjing, Gulou Hospital Group. We constructed a prediction model by using a support vector machine (SVM) classifier coupled with a least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO). We applied a 10-fold cross-validation to estimate the error rate for each model. RESULTS The present study indicated that acute symptomatic PVT was associated with 11 indicators, including liver cirrhosis, D-Dimer, splenomegaly, splenectomy, inherited thrombophilia, ascetic fluid, history of abdominal surgery, bloating, C-reactive protein (CRP), albumin and abdominal tenderness. The LASSO-SVM model achieved a sensitivity of 91.5% and a specificity of 100.0%. CONCLUSIONS We developed a LASSO-SVM model to diagnose PVT. We demonstrated that the model achieved a sensitivity of 91.5% and a specificity of 100.0%.
Journal Title: Annals of vascular surgery
Year Published: 2019
Link to full text (if available)
Share on Social Media: Sign Up to like & get
recommendations!